




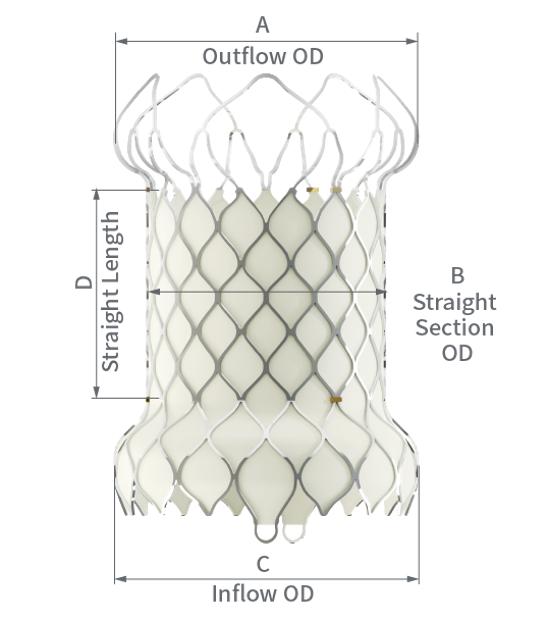
VenusP-Valve™ System
The VenusP-Valve™ System is the first self-expanding nitinol stent for the pulmonary valve recognized in Europe (Venus Medtech).
It is designed with valve diameters of 28–36 mm, specifically for large right ventricular outflow tracts (RVOTs).
The VenusP-Valve™ System is intended to replace the pulmonary heart valve with an artificial valve using a minimally invasive percutaneous approach, to treat right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) dysfunction and restore pulmonary valve function in dilated outflow tracts.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Known hypersensitivity or contraindication to aspirin, heparin, ticlopidine, clopidogrel, nitinol, or contrast media that cannot be adequately pre-medicated.
- Septicemia, including active endocarditis.
- Recent myocardial infarction (< 30 days).
- Echocardiographic evidence of intracardiac mass, thrombus, or vegetation.
- Any contraindication to extracorporeal assist devices (e.g., ECMO, CPB).
- Evolving or recent cerebral vascular accident (CVA).
- Obstruction of central veins.
- Bleeding diathesis, coagulopathy, or patient refusal of blood transfusion.
- Creatinine clearance (CCR) < 20 mL/min.
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding.
- Known allergy to porcine materials.
POTENTIAL RISKS
Associated with transfemoral access and general anesthesia:
- Death.
- Cardiovascular or vascular injury such as perforation or dissection of vessels, myocardium, or valvular structures requiring intervention.
- Arrhythmia.
- Pericardial effusion / cardiac tamponade.
- Perforation or damage of vessels.
- Air or thrombus embolization.
- Hematoma or hemorrhage requiring transfusion.
- Hypertension / hypotension.
- Infection, including endocarditis and septicemia.
- Systemic ischemia or nerve injury.
- Allergic reaction to contrast dye.
- Anesthesia-related complications.
- Radiation injury.
- Fever and systemic reactions.
Associated with the VenusP-Valve™ System:
- Myocardial infarction.
- Arteriovenous fistula.
- Bleeding.
- Coronary artery compression.
- Device embolization requiring intervention.
- Device explantation.
- Device migration or malposition requiring intervention.
- Device thrombosis requiring intervention.
- Emergency cardiac surgery.
- Endocarditis.
- Hemolysis / hemolytic anemia.
Important Information About Stent Fracture
In some patients, the wire frame (stent) of the VenusP-Valve™ System may fracture due to the mechanical forces inside the body.
In certain cases, the fractured stent may not require additional treatment.
However, patients should be aware that a stent fracture can potentially become serious and might require a reintervention.
The physician will determine the best treatment option.
In the VenusP-Valve™ System CE Clinical Interim Report, 11 stent fractures (14.5%) were identified, which did not affect valve functionality and required no additional treatment.